Remember you have a practice quiz until "SMELL" this Friday the 5th of November. Study and later, practice doing this quiz below.
PRACTICE QUIZ 2 (THE HUMAN BODY)
1- The bones that form the skull are:
2- It is a system that gives humans the
ability to move using their muscles and bones.
3- They connect muscles to bones at the
joint.
4- In what part of the skeleton are your
occipitals?
5- Is the knee a fixed joint?
6- Name four joints in your arm.
7- The largest bone in your body is
the...
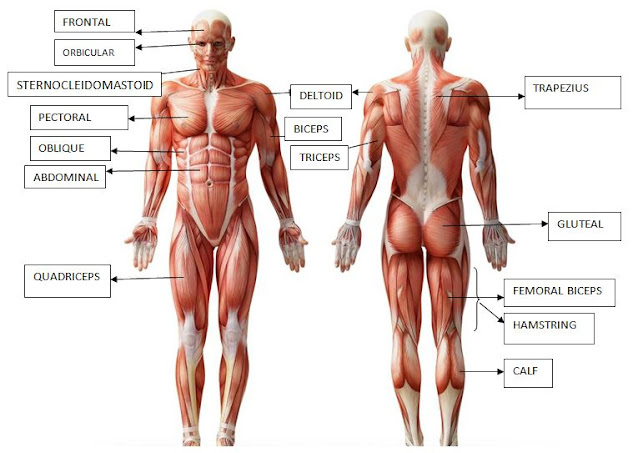
8- What are the names of the muscles in
your legs?
9- The three types of muscles are…
10- Stomach is an example of voluntary/involuntary
muscle.
11- Are biceps involuntary muscles?
12- Write two involuntary muscles.
13- What sense do we use to hear?
14- It is behind the pupil and the iris.
It focuses light on the retina.
15- Part of the eye which gives the colour
to the eye.
16- Part of the eye that lets light to
get in.
17- It is the organ of taste.
18- They are the two holes at the
entrance of your nose.
19- Nerve fibers are connected to the
___________ which sends information to the brain.
20- It is the sticky substance in your nose that
stops germs and dust.
21- They give us information about the
world around us.